If you are looking to gain knowledge about the cheque return reason list, you have come to the right place. In this article, we will provide you with a detailed overview of the various reasons behind cheque bounces or returns.
This information has been compiled after referring to more than 07 articles on this topic, ensuring that you receive accurate and reliable information.
CHEQUE BOUNCE REASONS
There are several reasons why cheques may bounce or be returned. Some of the common reasons include incorrect dates, insufficient funds in the payer’s bank account, signature mismatches, discrepancies between the written and numerical amounts, and more.
CHEQUE RETURN REASONS ARE CATEGORIZED INTO NINE TYPES
1. Funds
2. Reference to Drawer
3. Signature
4. Stop Payment by Drawer
5. Based on Instruments
6. Based on Account
7. Based on Crossing/Endorsement
8. Based on RBI/Government 9. Other Miscellaneous reasons
Let’s explain into each category and explore the specific reasons within them.

1. Funds Insufficient (Code No. 1)
This is the first cheque return reason. It indicates that the drawer’s account does not have enough balance to honor the cheque.
2. Exceeds Arrangement (Code No. 2)
This reason arises when the cheque amount exceeds the available balance in the drawer’s overdraft or cash credit account. In other words, the customer has fully utilized the funds in their account, making it insufficient to cover the cheque.
3. Effects Not Cleared, Present Again (Code No. 3)
This reason suggests that the drawer expects funds to be deposited into their account shortly. The payee is requested to present the cheque again after a certain period.
4. Refer to Drawer (Code No. 4)
When the cheque is returned with this reason, it means that the drawer has specified a particular reason to pay the cheque. The bank may not want to disclose the exact cause to protect the reputation of the drawer in the eyes of the payee.
5. Kindly Contact Drawer/Drawee Bank and Present Again in Clearing (Code No. 5)
This reason indicates that you need to contact the drawer or the drawee bank for any queries regarding the cheque. Once the query is resolved, you can present the cheque again for clearing.
6. Drawer’s Signature Incomplete (Code No. 10)
This reason code suggests that the drawer has not provided a complete signature on the cheque.
7. Drawer’s Signature Illegible (Code No. 11)
When the drawer’s signature is mismatched, wrong, or incomplete, the cheque may be returned with this reason code.
8. Drawer’s Signature Differs (Code No. 12)
This reason code is used when the drawer’s signature does not match the signature provided in the bank’s records.
9. Drawer’s Signature Required (Code No. 13)
If the drawer has not signed the cheque, it may be returned with this reason code.
10. Drawer’s Signature Not as Per Mandate (Code No. 14)
When the drawer’s signature differs from the mandate provided in the bank’s records, the cheque may be returned with this reason.
11. Drawer’s Signature to Operate Account Not Received (Code No. 15)
This reason indicates that the bank has not received an updated signature from the drawer to operate the account.
12. Drawer’s Authority to Operate Account Not Received (Code No. 16)
If the drawer has not provided any authority to the bank to make payments, the cheque may be returned with this reason code.
13. Alteration Requires Drawer’s Authentication (Code No. 17)
If there is any alteration in the cheque, that requires authentication by the drawer, it may be returned with this reason.
14. Payment Stopped by Drawer (Code No. 20)
When the drawer informs the bank to stop making payment of the cheque, it may be returned with this reason. The bank may charge a fee for stopping the payment.

15. Payment Stopped by Attachment Order (Code No. 21)
If the bank receives an attachment order from a government department, instructing them not to make any payment, the cheque may be returned with this reason.
16. Payment Stopped by Court Order (Code No. 22)
In cases where the bank receives a court order not to make any payment, the cheque may be returned with this reason.
17. Withdrawal Stopped Owing to Death of Account Holder (Code No. 23)
If the account holder has passed away, and the bank becomes aware of this during the clearing process, the cheque may be returned with this reason.
18. Withdrawal Stopped Owing to Lunacy of Account Holder (Code No. 24)
When the drawer is unable to confirm the payment of the cheque due to the lunacy of the account holder, the cheque may be returned with this reason.
19. Withdrawal Stopped Owing to Insolvency of Account Holder (Code No. 25)
If the drawer is unable to pay the cheque amount due to the account holder’s insolvency, the cheque may be returned with this reason.
20. Instrument Post-dated (Code No. 30)
A post-dated cheque is one that is created or signed for a future date. If a cheque is postdated, it is not considered valid for making payments until the specified date has arrived.
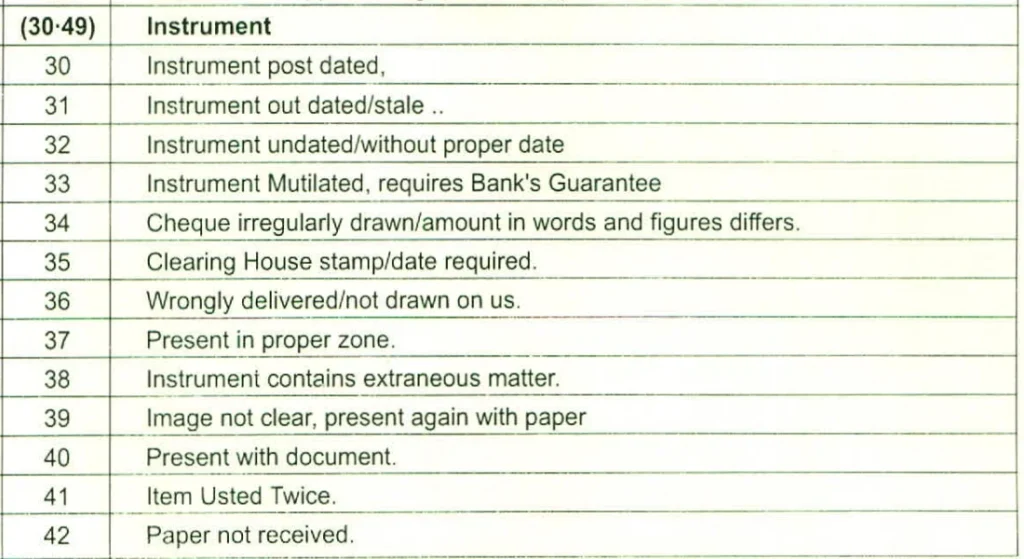
21. Instrument Outdated/Stale (Code No. 31)
If the date written on the cheque has already passed three months or 90 days, the cheque is considered outdated or stale and not valid for payment. However, in some cases, outdated/stale cheques may be used as evidence.
FAQS
What is reason 70 for cheque return?
Reason No 70 refers to Advice Not Received.
For 500000/ above cheque customer need to inform the banks but if customer not informed cheque may be returned with reason no. 70
What is reason 88 for cheque return?
It refers to the other reasons.
CONCLUSION ON CHEQUE RETURN REASON LIST
In this article, we provided a comprehensive guide to the cheque return reason list. It is crucial to understand these reasons as bouncing cheques can have legal and financial consequences. Cheque issuers are liable to pay penalties for such occurrences.
We hope this article has helped you gain a better understanding of the various cheque return reasons. If you have any further queries or require additional information, please feel free to leave a comment below.
ALSO READ
